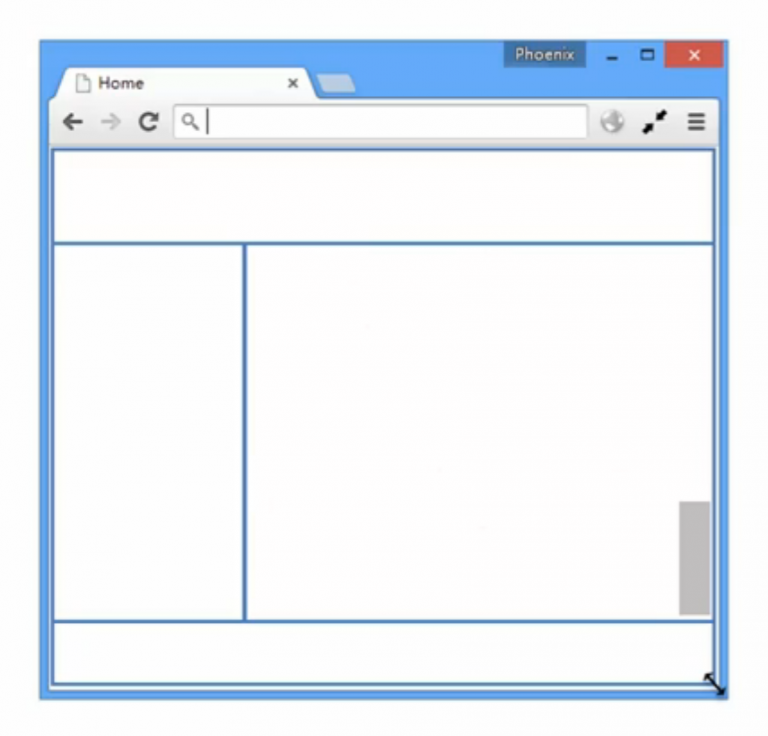
全屏布局
了解 CSS 中属性的值及其特性, 透彻分析问题和需求才可以选择和设计最适合的布局解决方案。
[ 全屏布局的特点 ] 例如,管理系统、监控与统计平台,均广泛的使用全屏布局。
- 滚动条不是全局滚动条,而是出现在内容区域里,往往是主内容区域
- 浏览器变大时,撑满窗口
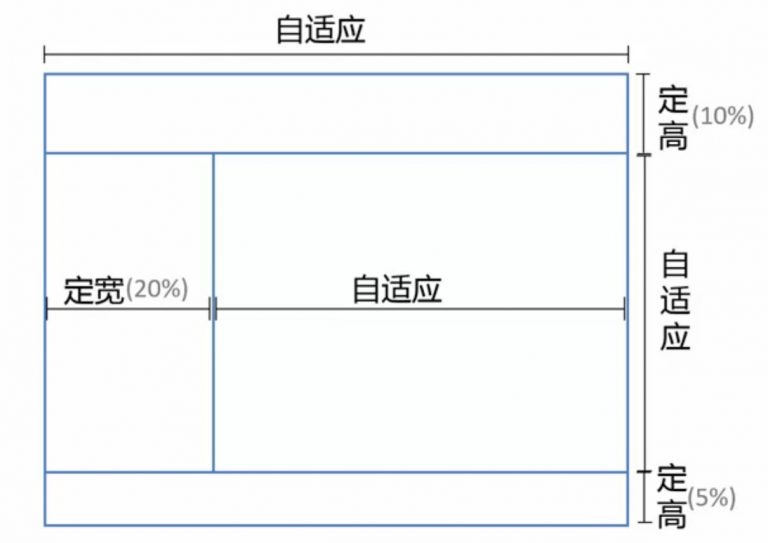
定宽需求
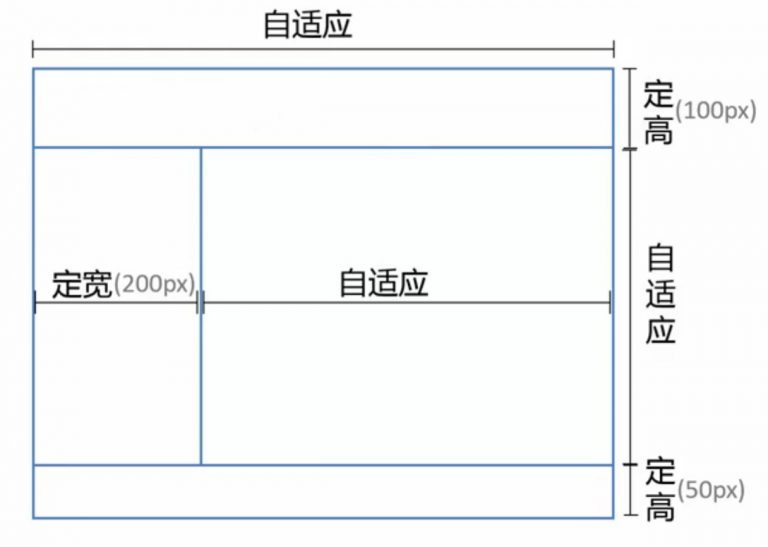
[1] position
[ 原理 ]将上下部分固定,中间部分使用定宽+自适应+两块高度一样高
<div class="parent">
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right">
/*辅助结构用于滚动*/
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
</div>
<style>
html,
body,
.parent {
height: 100%;
/*用于隐藏滚动条*/
overflo: hidden;
}
.top {
/*相对于 body 定位*/
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
height: 100px;
}
.left {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 100px;
bottom: 50px;
width: 200px;
}
.right {
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
right: 0;
top: 100px;
bottom: 50px;
overflow: auto;
}
.right .inner {
/*此样式为演示所有*/
min-height: 1000px;
}
.bottom {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
height: 50px;
}
</style>
// 优缺点:兼容性好,ie6下不支持
[ position 兼容 ] 此方法不支持 IE6 ,可以使用下面的方法解决兼容问题。
<div class="g-hd"></div> <div class="g-sd"></div> <div class="g-mn"></div> <div class="g-ft"></div> <style> html, body { width: 100%; height: 100%; overflow: hidden; margin: 0; } html { _height: auto; _padding: 100px 0 50px; } .g-hd, .g-sd, .g-mn, .g-ft { position: absolute; left: 0; } .g-hd, .g-ft { width: 100%; } .g-sd, .g-mn { top: 100px; bottom: 50px; _height: 100%; overflow: auto; } .g-hd { top: 0; height: 100px; } .g-sd { width: 300px; } .g-mn { _position: relative; left: 300px; right: 0; _top: 0; _left: 0; _margin-left: 300px; } .g-ft { bottom: 0; height: 50px; } </style>
[2] Flex
[ 原理 ] 通过灵活使用CSS3布局利器flex中的flex属性和flex-direction属性以达到全屏布局。
<div class="parent">
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="middle">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right">
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
</div>
<style media="screen">
html,
body,
parent {
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
.parent {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.top {
height: 100px;
}
.bottom {
height: 50px;
}
.middle {
// 居中自适应
flex: 1;
display: flex;
/*flex-direction: row 为默认值*/
}
.left {
width: 200px;
}
.right {
flex: 1;
overflow: auto;
}
.right .inner {
min-height: 1000px;
}
</style>
// 优缺点:兼容性差,ie9及ie9以下不兼容
百分比宽度需求
[ 原理及用法 ]只需把定宽高(
px为单位的值)的实现改成百分比(%)既可。
内容自适应
只有右侧栏占据剩余位置,其余空间均需根据内容改变。 所以 Postion 的定位方法不适合实现此方案。
[ Flex ] 只有不为宽高做出限制,既可对其中的内容做出自适应的布局。
<div class="parent">
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="middle">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right">
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
</div>
<style media="screen">
html,
body,
parent {
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
.parent {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.middle {
// 居中自适应
flex: 1;
display: flex;
/*flex-direction: row 为默认值*/
}
.right {
flex: 1;
overflow: auto;
}
.right .inner {
min-height: 1000px;
}
</style>