脚本化CSS
脚本化CSS,通俗点说,就是使用JavaScript来操作CSS。引入CSS有3种方式:外部样式,内部样式和行间样式。
脚本化行间样式
01. 基本用法
行间样式又叫内联样式,使用HTML的style属性进行设置。
<div style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color: blue;"></div>
element元素节点提供style属性,用来操作CSS行间样式,style属性指向cssStyleDeclaration对象。
[注意] IE7-浏览器不支持cssStyleDeclaration对象。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color: blue;"></div> <script> // IE7-浏览器返回报错,其他浏览器返回true console.log(test.style instanceof CSSStyleDeclaration); </script>
style属性用来读写页面元素的行内CSS样式。
如果读取没有设置过的行间样式将返回空字符串''。
如果设置的行间样式不符合预定格式,并不会报错,而是静默失败。
[注意] IE8-浏览器支持给属性设置值时不带单位。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color: blue;"></div> <script> console.log(test.style.height);//'40px' test.style.height = '30px'; console.log(test.style.height);//'30px' test.style.height = '20'; // IE8-浏览器返回'20px',因为IE8-浏览器支持给属性设置值时不带单位;而其他浏览器仍然返回'30px' console.log(test.style.height); console.log(test.style.position);//'' </script>
如果一个CSS属性名包含一个或多个连字符,CSSStyleDeclaration属性名的格式应该是移除连字符,将每个连字符后面紧接着的字母大写。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color: blue;"></div> <script> console.log(test.style.backgroundColor);//'blue' </script>
float
理论上,有一个不能直接转换的CSS属性是float。因为,float是javascript中的保留字,不能用作属性名。
但实际上,经过测试,直接使用float在各个浏览器中都有效。
<div id="test" style="float:left"></div> <script> console.log(test.style.float);//'left' </script>
作为推荐,要访问float属性,应该使用cssFloat。
[注意] IE8-浏览器不支持cssFloat,但IE浏览器支持styleFloat。
<div id="test" style="float:left"></div> <script> //IE8-浏览器返回undefined,其他浏览器返回'left' console.log(test.style.cssFloat);//'left' //IE浏览器返回'left',其他浏览器返回undefined console.log(test.style.styleFloat); </script>
特性操作
其实,如果操作行间样式,可以使用元素节点的特性操作方法hasAttribute()、getAttribute()、setAttribute()、removeAttribute()等,来操作style属性。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;"></div>
<script>
console.log(test.hasAttribute('style'));//true
console.log(test.getAttribute('style'));//'height: 40px;width: 40px;'
test.setAttribute('style','height:10px;');
console.log(test.getAttribute('style'));//'height:10px;'
test.removeAttribute('style');
console.log(test.hasAttribute('style'));//false
console.log(test.getAttribute('style'));//null
</script>
02. 属性
cssText
通过cssText属性能够访问到style特性中的CSS代码。在读模式下,cssText返回浏览器对style特性中CSS代码的内部表示;在写模式中,赋给cssText的值会重写整个style特性的值。
设置cssText是为元素应用多项变化最快捷的方法,因为可以一次性应用所有变化。
[注意]IE8-浏览器返回的属性名是全大写的。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;"></div> <script> //IE8-浏览器返回'HEIGHT: 40px; WIDTH: 40px;',其他浏览器返回'height: 40px; width: 40px;' console.log(test.style.cssText); test.style.cssText= 'height:20px'; //IE8-浏览器返回'HEIGHT: 20px;',其他浏览器返回'height: 20px;' console.log(test.style.cssText); </script>
length
length属性返回内联样式中的样式个数。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;"></div> <script> console.log(test.style.length);//2 </script>
parentRule
parentRule属性表示CSS信息的CSSRule对象。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;"></div> <script> //IE8-浏览器返回undefined,其他浏览器返回null console.log(test.style.parentRule); </script>
03. 方法
item()
item()方法返回给定位置的CSS属性的名称,也可以使用方括号语法。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持item()方法,只支持方括号语法。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color: pink;"></div> <script> //IE9+浏览器返回'width',IE8-浏览器报错,其他浏览器返回'height' console.log(test.style.item(0)); //IE9+浏览器返回'width',IE8-浏览器返回'WIDTH',其他浏览器返回'height' console.log(test.style[0]) </script>
由上面代码可知,IE浏览器返回值与其他浏览器有差异。
getPropertyValue()
getPropertyValue()方法返回给定属性的字符串值。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color: pink;"></div>
<script>
//IE8-浏览器报错,其他浏览器返回'pink'
console.log(test.style.getPropertyValue('background-color'));
console.log(test.style.backgroundColor);//'pink'
console.log(test.style['background-color']);//'pink'
console.log(test.style['backgroundColor']);//'pink'
</script>
getPropertyCSSValue()
getPropertyCSSValue()方法返回包含两个属性的CSSRule类型,这两个属性分别是cssText和cssValueType。其中cssText属性的值与getPropertyValue()返回的值相同,而cssValueType属性则是一个数值常量,表示值的类型:0表示继承的值,1表示基本的值,2表示值列表,3表示自定义的值。
[注意]该方法只有safari支持。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color: pink;"></div>
<script>
//cssText:"rgb(255, 192, 203)" cssValueType: 1 primitiveType: 25
console.log(test.style.getPropertyCSSValue('background-color'));
console.log(test.style.getPropertyCSSValue('background'));//null
</script>
getPropertyPriority()
如果给定的属性使用了!important设置,则返回"important";否则返回空字符串。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px!important;width: 40px;background-color: pink;"></div>
<script>
console.log(test.style.getPropertyPriority('height'));//'important'
console.log(test.style.getPropertyPriority('width'));//''
</script>
setProperty()
setProperty(propertyName,value,priority)方法将给定属性设置为相应的值,并加上优先级标志("important"或一个空字符串),该方法无返回值。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color: pink;"></div>
<script>
console.log(test.style.height);//'40px'
test.style.setProperty('height','20px','important');
console.log(test.style.height);//'20px'
test.style.setProperty('height','30px');
//safari浏览器返回'20px',设置过!important后,再设置非important的属性值则无效
//其他浏览器返回'30px'
console.log(test.style.height);
</script>
removeProperty()
removeProperty()方法从样式中删除给定属性,并返回被删除属性的属性值。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<div id="test" style="height: 40px;width: 40px;background-color: pink;"></div>
<script>
console.log(test.style.height);//'40px'
console.log(test.style.removeProperty('height'));//'40px'
console.log(test.style.height);//''
console.log(test.style.width);//'40px'
test.style.width = '';
console.log(test.style.width);//''
</script>
模块侦测
CSS的规格发展太快,新的模块层出不穷。不同浏览器的不同版本,对CSS模块的支持情况都不一样。有时候,需要知道当前浏览器是否支持某个模块,这就叫做“CSS模块的侦测”。
一个比较普遍适用的方法是,判断某个DOM元素的style对象的某个属性值是否为字符串。如果该CSS属性确实存在,会返回一个字符串。即使该属性实际上并未设置,也会返回一个空字符串。如果该属性不存在,则会返回undefined。
<div id="test"></div> <script> //IE9-浏览器和safari返回undefined,其他浏览器都返回'',所以IE9-浏览器和safari不支持animation console.log(test.style.animation) //IE和firefox浏览器返回undefined,chrome和safari浏览器都返回'',所以IE和firefox浏览器不支持WebkitAnimation console.log(test.style.WebkitAnimation) </script>
CSS.supports()
CSS.supports()方法返回一个布尔值,表示是否支持某条CSS规则。
[注意]safari和IE浏览器不支持。
<script>
//chrome和firefox浏览器返回true,其他浏览器报错
console.log(CSS.supports('transition','1s'));
</script>
查询计算样式
元素的渲染结果是多个CSS样式博弈后的最终结果,这也是CSS中的C(cascade)层叠的含义。访问style属性只能获取行间样式,这通常来说,并不是我们想要的结果。
一般,我们通过getComputedStyle()方法或currentStyle属性获得元素的计算样式,但要获得元素精确的位置和尺寸信息,查询元素计算样式并不是个好主意,类似padding、width等单一样式并不直接反映元素的位置和尺寸信息,这些信息是多个样式综合作用的结果。所以,最好使用元素视图的offset、client、scroll和getBoundingClientRect()等来获取。
01. getComputedStyle()
元素的计算样式(computedStyle)是一组在显示元素时实际使用的属性值,也是用一个 CSSStyleDeclaration对象来表示的,但计算样式是只读的,主要通过getComputedStyle()方法实现
getComputedStyle()方法接收两个参数:要取得计算样式的元素和一个伪元素字符串。如果不需要伪元素信息,第二个参数可以是null。getComputedStyle()方法返回一个CSSStyleDeclaration对象,其中包含当前元素的所有计算的样式
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持
getComputedStyle()方法原本是window对象下的方法,后来“DOM2级样式”增强了document.defaultView,也提供了getComputedStyle()方法。所以getComputedStyle()方法一共有下面3种写法
1、document.defaultView.getComputedStyle(div).width
2、window.getComputedStyle(div).width
3、getComputedStyle(div).width
其中第3种写法最简单。
<div id="test" style="width: 100px;"></div> <script> //下面三行代码的结果都一样,IE8-浏览器报错,其他浏览器返回'100px' console.log(document.defaultView.getComputedStyle(test).width); console.log(window.getComputedStyle(test).width); console.log(getComputedStyle(test).width); </script>
伪元素
第二个参数代表伪元素字符串,包括":before"、":after"、":first-line"等,如果设置为null或省略不写,则返回自身元素的CSSStyleDeclaration对象。
<style>
#test:before{
content:'';
width:20px;
display:inline-block;
}
</style>
<div id="test" style="width: 100px;"></div>
<script>
//IE8-浏览器报错,其他浏览器返回'20px'
console.log(getComputedStyle(test,':before').width);
</script>
02. 注意事项
在使用getComputedStyle()方法的过程中,有如下注意事项:
【1】对于font、background、border等复合样式,各浏览器处理不一样。chrome会返回整个复合样式,而IE9+、firefox和safari则输出空字符串''。
<div id="test" style="font-size:20px"></div> <script> //IE8-浏览器报错,chrome返回normal normal normal normal 20px / normal Simsun,其他浏览器返回'' console.log(getComputedStyle(test).font); </script>
【2】不论以什么格式设置颜色,浏览器都以rgb()或rgba()的形式输出。
<div id="test" style="color:red"></div> <script> //IE8-浏览器报错,其他浏览器返回rgb(255, 0, 0) console.log(getComputedStyle(test).color); </script>
【3】在计算样式中,类似百分比等相对单位会转换为绝对值。
<div id="test" style="width:20%;"></div> <script> // IE8-浏览器报错,其他浏览器返回'304px' console.log(getComputedStyle(test).width); </script>
03. currentStyle
IE8-浏览器不支持getComputedStyle()方法,但在IE中每个具有style属性的元素有一个currentStyle属性,这个属性是CSSStyleDeclaration的实例,包含当前元素全部计算后的样式。
<div id="test" style="font-size:20px;color:red;width:20%;"></div> <script> // IE8-浏览器返回undefined,IE9+浏览器返回'' console.log(test.currentStyle.font); // IE浏览器返回red console.log(test.currentStyle.color); // IE浏览器返回20% console.log(test.currentStyle.width); </script>
由以上结果看出,currentStyle属性中的计算样式并不会输出集合样式,对颜色、百分比设置不会进行相应转换,而是原样输出。
兼容
function getCSS(obj,style){
if(window.getComputedStyle){
return getComputedStyle(obj)[style];
}
return obj.currentStyle[style];
}
<div id="test" style="width:20px;"></div>
<script>
function getCSS(obj,style){
if(window.getComputedStyle){
return getComputedStyle(obj)[style];
}
return obj.currentStyle[style];
}
console.log(getCSS(test,'width'));//20px
</script>
04. IE
IE9+浏览器的getComputedStyle()方法和IE浏览器的currentStyle属性有一个特别的地方,就是可以识别自定义样式的值,虽然无法正常渲染,但是可以取出值。
<div id="test" style="a:1"></div> <script> //其他浏览器输出undefined,而IE9+浏览器输出1 console.log(getComputedStyle(test).a); //其他浏览器输出undefined,而IE浏览器输出1 console.log(test.currentStyle.a); </script>
opacity
虽然IE8-浏览器无法对opacity属性进行正常渲染,但可以读出opacity属性的值。这对于opacity属性来说无疑是一个好消息。
<div id="test" style="opacity:0.5"></div>
<script>
function getCSS(obj,style){
if(window.getComputedStyle){
return getComputedStyle(obj)[style];
}
return obj.currentStyle[style];
}
console.log(getCSS(test,'opacity'));//0.5
</script>
脚本化CSS类
在实际工作中,我们使用javascript操作CSS样式时,如果要改变大量样式,会使用脚本化CSS类的技术。
01. style
我们在改变元素的少部分样式时,一般会直接改变其行间样式。
<div id="test" style="height:100px;width:100px;background-color:blue;"></div>
<script>
test.onclick = function(){
test.style.backgroundColor = 'green';
}
</script>
02. cssText
改变元素的较多样式时,可以使用cssText。
<div id="test" style="height:100px;width:100px;background-color:blue;"></div>
<script>
test.onclick = function(){
test.style.cssText = 'height:50px;width:50px;background-color:green';
}
</script>
03. css类
更常用的是使用css类,将更改前和更改后的样式提前设置为类名。只要更改其类名即可。
<style>
.big{
height:100px;
width:100px;
background-color:blue;
}
.small{
height:50px;
width:50px;
background-color:green;
}
</style>
<div id="test" class="big"></div>
<script>
test.onclick = function(){
test.className = 'small';
}
</script>
04. classList
如果要改变多个类名,使用classList更为方便。[注意] IE9-浏览器不支持。
<style>
.big{
height:100px;
width:100px;
}
.small{
height:50px;
width:50px;
}
.green{
background-color:green;
}
.blue{
background-color:blue;
}
</style>
<div id="test" class="big green"></div>
<button id="btn1">大小变化</button>
<button id="btn2">颜色变化</button>
<script>
btn1.onclick = function(){
test.classList.toggle('small');
}
btn2.onclick = function(){
test.classList.toggle('blue');
}
</script>
05. 性能
<div id="test" style="height:100px;width:100px;background-color:blue;"></div>
<script>
test.onclick = function(){
console.time();
for(var i = 0; i < 10000; i++){
test.style.backgroundColor = 'green';
test.style.height = '50px';
test.style.width = '50px';
}
console.timeEnd();//59.937ms
}
</script>
/*****************************/
<div id="test" style="height:100px;width:100px;background-color:blue;"></div>
<script>
test.onclick = function(){
console.time();
for(var i = 0; i < 10000; i++){
test.style.cssText = 'height:50px;width:50px;background-color:green';
}
console.timeEnd();//38.065ms
}
</script>
/*****************************/
<style>
.big{
height:100px;
width:100px;
background-color:blue;
}
.small{
height:50px;
width:50px;
background-color:green;
}
</style>
<div id="test" class="big"></div>
<script>
test.onclick = function(){
console.time();
for(var i = 0; i < 10000; i++){
test.className = 'small';
}
console.timeEnd();//9.534ms
}
</script>
在1万次循环中,改变style属性中的具体样式花费了59.937ms,改变style属性中的cssText花费了38.065ms,而改变css类名只花费了9.534ms。
由此可见,使用脚本化CSS类的方式可以大大地提高性能。
脚本化样式表
关于脚本化CSS,查询样式时,查询的是计算样式;设置单个样式时,设置的是行间样式;设置多个样式时,设置的是CSS类名。脚本化样式表当然也是一种脚本化CSS的技术,虽然不经常使用,但有时却非常有用。
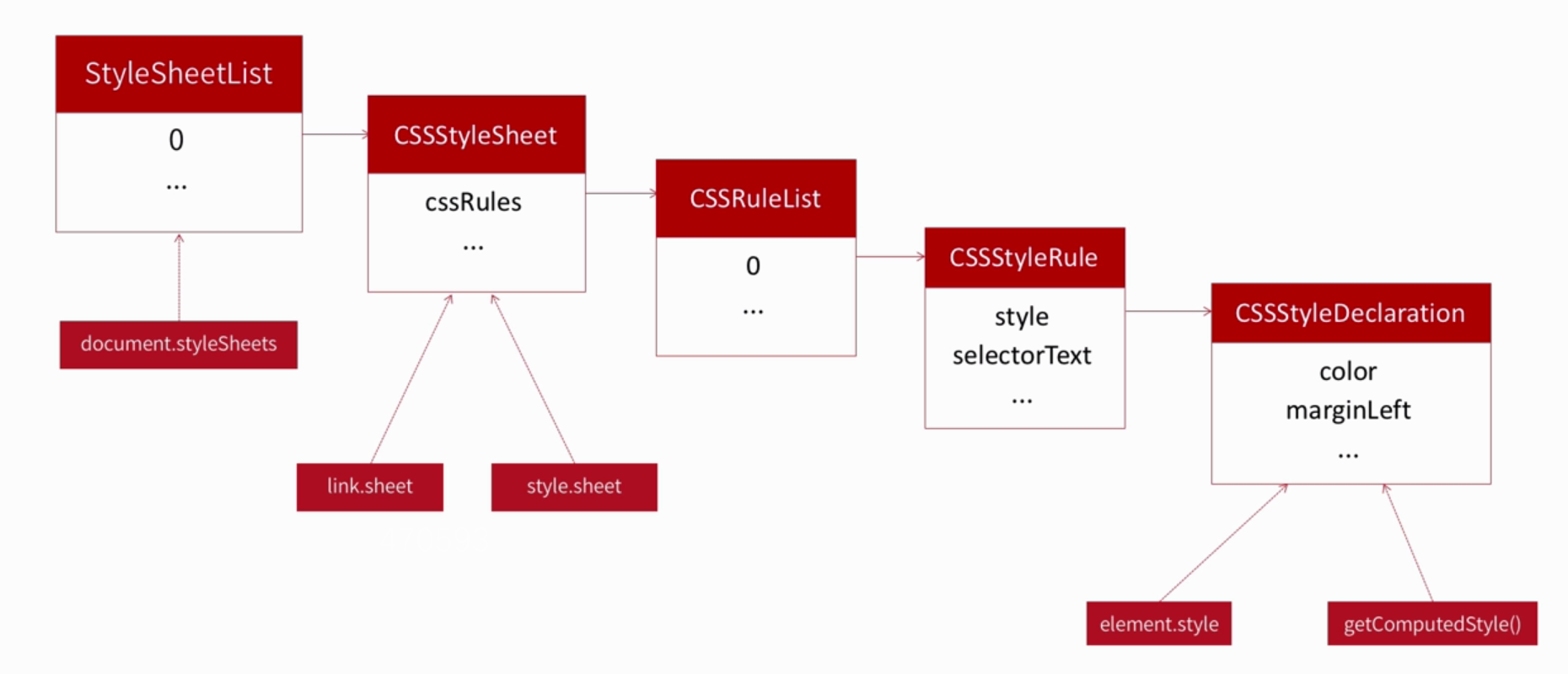
01. CSSStyleSheet
CSSStyleSheet类型表示的是样式表。我们知道,引入CSS一共有3种方式,包括行间样式、内部样式和外部样式。其中,内部样式和外部样式分别通过<style>和<link>标签以样式表的形式引入,属于CSSStyleSheet类型。
styleSheet
CSSStyleSheet对象只是一个类数组对象,它继承自Stylesheet。
样式表CSSStyleSheet是通过document.styleSheets集合来表示的。通过集合的length属性可以获知样式表的数量,而通过方括号语法或item()方法可以访问毎一个样式表。
<style id="styleIn1"></style> <script> console.log(document.styleSheets[0] instanceof StyleSheet);//true console.log(document.styleSheets[0] instanceof CSSStyleSheet);//true </script>
<style id="styleIn1"></style>
<link id="styleOut" rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<style id="styleIn2"></style>
<script>
console.log(document.styleSheets.length);//3
//CSSStyleSheet {ownerRule: null, cssRules: CSSRuleList, rules: CSSRuleList, type: "text/css", href: null…}
console.log(document.styleSheets[0]);
//CSSStyleSheet {ownerRule: null, cssRules: null, rules: null, type: "text/css", href: "file:///C:/inetpub/wwwroot/style.css"…}
console.log(document.styleSheets[1]);
</script>
引入
除了使用document.styleSheets,还可以通过<link>或<style>元素的sheet属性,取得CSSStyleSheet对象。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<style id="test"></style>
<script>
//CSSStyleSheet {ownerRule: null, cssRules: CSSRuleList, rules: CSSRuleList, type: "text/css", href: null…}
console.log(test.sheet);
console.log(test.sheet=== document.styleSheets[0]);//true
</script>
IE10-浏览器支持<link>或<style>元素的styleSheet属性,来取得CSSStyleSheet对象。
<style id="test"></style> <script> //[object CSSStyleSheet] console.log(test.styleSheet); </script>
兼容
function getSheet(element){
return element.sheet || element.styleSheet;
}
继承属性
从Stylesheet接口继承而来的属性如下
【1】disabled
disabled表示样式表是否被禁用的布尔值。这个属性是可读/写的,将这个值设置为true可以禁用样式表。
<style id="styleIn1">
#test{background-color: red!important;}
</style>
<div id="test" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: black;"></div>
<button id="btn1">变色</button>
<script>
btn1.onclick = function(){
document.styleSheets[0].disabled = !document.styleSheets[0].disabled;
}
</script>
【2】href
如果样式表是通过<link>包含的,则表示样式表的URL;否则,是null。
<style id="styleIn1"></style> <link id="styleOut" rel="stylesheet" href="style.css"> <script> console.log(document.styleSheets[0].href);//null //file:///C:/inetpub/wwwroot/style.css console.log(document.styleSheets[1].href); </script>
【3】media
media属性表示当前样式表支持的所有媒体类型的集合MediaList。与所有DOM集合一样,这个集合也有一个length属性和一个item()方法。也可以使用方括号语法取得集合中特定的项。如果集合是空列表,表示样式表适用于所有媒体。在IE8-浏览器中,media是一个反映<link>和<style>元素media特性值的字符串。
<style media="all and (min-width:100px)">
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color: pink;}
</style>
<script>
//IE8-浏览器返回'all and (min-width:100px)'
//其他浏览器返回MediaList [ "all and (min-width: 100px)" ]
console.log(document.styleSheet[0].media);
</script>
【4】ownerNode
ownerNode属性返回StyleSheet对象所在的DOM节点,通常是<link>或<style>。如果当前样式表是其他样式表通过@import导入的,则这个属性值为null。
[注意] IE8-浏览器不支持这个属性。
<style id="test"></style> <script> //<style id="test"></style>,IE8-浏览器返回undefined console.log(document.styleSheets[0].ownerNode); </script>
【5】parentStyleSheet
parentStyleSheet表示在当前样式表是通过@import导入的情况下,这个属性是一个指向导入它的样式表的指针;否则为null。
<style id="test"></style> <script> console.log(document.styleSheets[0].parentStyleSheet);//null </script>
【6】title
title属性表示ownerNode中title属性的值。
<style title="test"></style> <script> console.log(document.styleSheets[0].title);//test </script>
【7】type
type属性表示样式表类型的字符串。对CSS样式表而言,这个字符串是"type/css"。
<style type="text/css"></style> <script> console.log(document.styleSheets[0].type);//'text/css' </script>
[注意] 若省略type属性,默认为'text/css',但IE8-浏览器输出''。
<style></style> <script> //IE8-浏览器输出'',其他浏览器输出'text/css' console.log(document.styleSheets[0].type); </script>
【8】cssText
cssText属性返回样式表中所有样式的字符串表示,该属性可读写,常常用于动态样式的IE浏览器兼容处理。
[注意]该属性只有IE浏览器支持。
<style id="test">
.box{height: 100px;}
div{height: 100px;}
</style>
<script>
var sheet = test.sheet || test.styleSheet;
//IE浏览器返回'.box{height: 100px;} div{height: 100px;}'
//firefox浏览器报错
//其他浏览器返回undefined
console.log(sheet.cssText);
</script>
上面8个属性中,除了disabled属性和cssText属性之外,其他属性都是只读的。
自有属性和方法
【1】cssRules
cssRules属性表示样式表中包含的样式规则的集合。
<style>
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
//CSSRuleList {0: CSSStyleRule, length: 1}
console.log(document.styleSheets[0].cssRules);
</script>
IE8-浏览器不支持cssRules属性,但有一个类似的rules属性。
[注意] firefox不支持rules属性。
<style>
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
//CSSRuleList {0: CSSStyleRule, length: 1}
console.log(document.styleSheets[0].rules);
</script>
兼容
function rules(sheet){
return sheet.cssRules || sheet.rules;
}
【2】ownerRule
如果样式表是通过@import导入的,ownerRule属性就是一个指针,指向表示导入的规则;否则,值为null。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持这个属性。
<style>
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
console.log(document.styleSheets[0].ownerRule);//null
</script>
CSSStyleSheet对象的方法包括insertRule()、addRule()、deleteRule()和removeRule(),都用于操作CSSRule对象。
02. CSSRule对象
CSSRule对象表示样式表中的每一条规则。实际上,CSSRule是一个供其他多种类型继承的基类型,其中最常见的就是CSSStyleRule类型,表示样式信息。其他规则还包括@import、@font-face、@page和@charset。
CSSRule对象的列表通过CSSStyleSheets对象的cssRules属性或ruls属性得到。
<style>
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
//CSSStyleRule {selectorText: ".box", style: CSSStyleDeclaration, type: 1, cssText: ".box { height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: pink; }", parentRule: null…}
console.log(document.styleSheets[0].cssRules[0] || document.styleSheets[0].rules[0]);
</script>
属性
CSSStyleRule对象包含下列属性:
【1】cssText
cssText属性返回整条规则对应的文本。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<style id="test">
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
var sheet = test.sheet || test.styleSheet;
var rules = sheet.cssRules|| sheet.rules;
//'.box { height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: pink; }'
console.log(rules[0].cssText);
</script>
【2】style
style属性返回一个CSSStyleDeclaration对象,通过它设置和取得规则中特定的样式值。
这个CSSStyleDeclaration对象与行内元素的style属性的CSSStyleDeclaration对象类似,具有相似的属性和方法。
<style id="test">
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
var sheet = test.sheet || test.styleSheet;
var rules = sheet.cssRules || sheet.rules;
//CSSStyleDeclaration {0: "height", 1: "width", 2: "background-color", alignContent: "", alignItems: "", alignSelf: "", alignmentBaseline: "", all: ""…}
console.log(rules[0].style);
/*[注意]style属性下在cssText与CSSStyleRule对象下的cssText属性不同 ,前者只报包含样式信息,后者还包含选择符文本和围绕样式信息的花括号*/
//'height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: pink;'
console.log(rules[0].style.cssText)
//'.box { height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: pink; }'
console.log(rules[0].cssText)
</script>
【3】selectorText
selectorText属性返回当前规则的选择符文本。
<style id="test">
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
var sheet = test.sheet || test.styleSheet;
var rules = sheet.cssRules|| sheet.rules;
console.log(rules[0].selectorText);//'.box'
</script>
【4】parentRule
如果当前规则是导入的规则,这个属性引用的就是导入规则;否则,这个值为null。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<style id="test">
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
var sheet = test.sheet || test.styleSheet;
var rules = sheet.cssRules|| sheet.rules;
console.log(rules[0].parentRule);//null
</script>
【5】parentStyleSheet
parentStyleSheet属性表示当前规则所属的样式表。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<style>
.box{width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
var rules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules|| document.styleSheets[0].rules;
//CSSStyleSheet {ownerRule: null, cssRules: CSSRuleList, rules: CSSRuleList, type: "text/css", href: null…}
console.log(rules[0].parentStyleSheet);
</script>
【6】type
type属性返回有一个整数值,表示当前规则的类型。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
最常见的类型有以下几种。
1:样式规则,部署了CSSStyleRule接口 3:输入规则,部署了CSSImportRule接口 4:Media规则,部署了CSSMediaRule接口 5:字体规则,部署了CSSFontFaceRule接口
<style>
.box{width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<script>
var rules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules|| document.styleSheets[0].rules;
console.log(rules[0].type);//1
</script>
方法
CSSStyleRule对象本身并没有方法,操作CSSStyleRule对象的方法位于CSSStyleSheet对象中。
【1】添加规则
insertRule()
insertRule(rule,index)方法表示向cssRules集合中指定的位置插入rule字符串,并返回当前样式表的索引值。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<style>
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<div class="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">文字变红</button>
<script>
var rules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules || document.styleSheets[0].rules;
//'.box { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; }'
console.log(rules[0].cssText);
btn.onclick = function(){
console.log(document.styleSheets[0].insertRule('div{color:red;}',0));//0
console.log(rules[0].cssText);//'div { color: red; }'
}
</script>
虽然,IE8-浏览器不支持insertRule()方法,但支持类似的addRule()方法。
addRule(ruleKey,ruleValue,index)方法表示向cssRules集合中指定的位置插入rule字符串,并返回-1。
[注意] firefox不支持。
<style>
.box{height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color:pink;}
</style>
<div class="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">文字变红</button>
<script>
var rules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules || document.styleSheets[0].rules;
//'.box { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; }'
console.log(rules[0].cssText);
btn.onclick = function(){
console.log(document.styleSheets[0].addRule('div','color:red',0));//-1
console.log(rules[0].cssText);//'div { color: red; }'
}
</script>
兼容
function insertRule(sheet,ruleKey,ruleValue,index){
return sheet.insertRule ? sheet.insertRule(ruleKey+ '{' + ruleValue + '}',index) : sheet.addRule(ruleKey,ruleValue,index);
}
【2】删除规则
deleteRule()
deleteRule(index)方法删除cssRules集合中指定位置的规则,无返回值。
[注意]IE8-浏览器不支持。
<style>
.box{background-color:pink;}
.box{width: 100px;height: 100px;}
</style>
<div class="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">删除颜色</button>
<script>
var rules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules || document.styleSheets[0].rules;
//'.box { background-color: pink; }'
console.log(rules[0].cssText);
btn.onclick = function(){
console.log(document.styleSheets[0].deleteRule(0));//undefined
//.box { width: 100px; height: 100px; }
console.log(rules[0].cssText);
}
</script>
虽然,IE8-浏览器不支持deleteRule()方法,但支持类似的removeRule()方法。
removeRule(index)方法删除cssRules集合中指定位置的规则,无返回值。
[注意] firefox不支持。
<style>
.box{background-color:pink;}
.box{width: 100px;height: 100px;}
</style>
<div class="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">删除颜色</button>
<script>
var rules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules || document.styleSheets[0].rules;
//'.box { background-color: pink; }'
console.log(rules[0].cssText);
btn.onclick = function(){
console.log(document.styleSheets[0].removeRule(0));//undefined
//.box { width: 100px; height: 100px; }
console.log(rules[0].cssText);
}
</script>
兼容
function deleteRule(sheet,index){
(typeof sheet.deleteRule == "function")? sheet.deleteRule(index) : sheet.removeRule(index);
}
动态样式
很多时候,DOM操作比较简单明了,因此用javascript生成那些通常原本是HTML代码生成的内容并不麻烦。但由于浏览器充斥着隐藏的陷阱和不兼容问题,处理DOM中的某些部分时要复杂一些,比如动态样式就相对较复杂
所谓动态样式,是指在页面加载时并不存在,在页面加载完成后动态添加到页面的样式
动态样式包括两种情况:一种是通过<link>元素插入外部样式表,另一种是通过<style>元素插入内部样式。
01. 外部样式
/*style.css里面的内容*/
.box{height:100px;width:100px;background-color: pink;}
var link = document.createElement("link");
link.rel = "stylesheet";
link.type = "text/css";
link.href = "style.css";
var head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
head.appendChild(link);
使用函数封装如下:
<div class="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">动态添加样式</button>
<script>
function loadStyles(url){
loadStyles.mark = 'load';
var link = document.createElement("link");
link.rel = "stylesheet";
link.type = "text/css";
link.href = url;
var head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
head.appendChild(link);
}
btn.onclick = function(){
if(loadStyles.mark != 'load'){
loadStyles("style.css");
}
}
</script>
02. 内部样式
var style = document.createElement("style");
style.type = "text/css";
style.innerHTML = ".box{height:100px;width:100px;background-color: pink;}";
var head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
head.appendChild(style);
使用函数封装如下:
<div class="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">动态添加样式</button>
<script>
function loadStyles(str){
loadStyles.mark = 'load';
var style = document.createElement("style");
style.type = "text/css";
style.innerHTML = str;
var head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
head.appendChild(style);
}
btn.onclick = function(){
if(loadStyles.mark != 'load'){
loadStyles(".box{height:100px;width:100px;background-color: pink;}");
}
}
</script>
[注意]该方法在IE8-浏览器中报错,因为IE8-浏览器将<style>视为当作特殊的节点,不允许访问其子节点或设置innerHTML属性。
03. 兼容写法
动态插入内部样式时,存在兼容问题,下面有两种兼容处理办法:
兼容一
IE浏览器支持访问并修改元素的CSSStyleSheet对象的cssText属性,通过修改该属性可实现类似效果。
<div class="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">动态添加样式</button>
<script>
function loadStyles(str){
loadStyles.mark = 'load';
var style = document.createElement("style");
style.type = "text/css";
try{
style.innerHTML = str;
}catch(ex){
style.styleSheet.cssText = str;
}
var head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
head.appendChild(style);
}
btn.onclick = function(){
if(loadStyles.mark != 'load'){
loadStyles(".box{height:100px;width:100px;background-color: pink;}");
}
}
</script>
兼容二
作用域元素是微软自己的一个定义,一般来说页面中看到的元素是有作用域的元素,页面中看不到的元素就是无作用域的元素 。
在IE8-浏览器中,<style>元素是一个没有作用域的元素,如果通过innerHTML插入的字符串开头就是一个无作用域的元素,那么IE8-浏览器会在解析这个字符串前先删除该元素。
所以,下面这段代码是无效的。
div.innerHTML = '<style>div{height:100px;}</style>';
于是,可以通过增加一个'_'文本节点,然后再删除使之有效
div.innerHTML = "_<style>div{height:100px;}</style>";
div.removeChild(div.firstChild);
<div class="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">动态添加样式</button>
<script>
function loadStyles(str){
loadStyles.mark = 'load';
var div = document.createElement("div");
div.innerHTML = '_' + '<style>' + str+'</style>';
div.removeChild(div.firstChild);
var head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
head.appendChild(div.firstChild);
div = null;
}
btn.onclick = function(){
if(loadStyles.mark != 'load'){
loadStyles(".box{height:100px;width:100px;background-color: pink;}");
}
}
</script>
脚本化伪元素
我们可以通过计算样式来读取伪元素的样式信息,但是却无法使用javascript来直接操作伪元素,以下一个需求解决为例,介绍脚本化伪元素的6种方法。
需求说明
【1】为id=box的div元素添加content="前缀"的:before伪元素。
【2】为已经添加:before伪元素的div元素删除伪元素。
[注意]由于IE7-浏览器不支持:before伪元素,所以该需求兼容到IE8。
01. 添加伪元素
[1] 动态样式
可以采用动态样式的方法,动态生成<style>标签及相关的伪元素样式内容。
由于IE8-浏览器将<style>标签当作特殊的节点,不允许访问其子节点及设置innerHTML属性,需要使用CSSStyleSheet对象的cssText属性来实现兼容。
<div id="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">添加伪元素</button>
<script>
//添加伪元素
function loadStyles(str){
//设置标记,防止重复添加
loadStyles.mark = 'load';
var style = document.createElement("style");
style.type = "text/css";
try{
style.innerHTML = str;
}catch(ex){
//IE8-浏览器兼容
style.styleSheet.cssText = str;
}
var head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
head.appendChild(style);
}
btn.onclick = function(){
//当样式表没有添加过时,添加
if(loadStyles.mark != 'load'){
loadStyles("#box:before{content:'前缀';color: red;}");
}
}
</script>
[2] 添加自带伪元素的类名
在处理大量CSS样式时,一般采用脚本化CSS类的方法。而添加伪元素,也可以使用类似的技术。把伪元素的样式挂在一个新类名上,然后把元素的className设置为新类名。
<style>
.add:before{content: "前缀";color: blue;}
</style>
<div id="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">添加伪元素</button>
<script>
btn.onclick = function(){
box.className = 'add';
}
</script>
[3] 利用setAttribute()方法实现自定义伪元素内容
若使用方法二,无法自定义伪元素的内容,拓展性不高。
伪元素的content属性非常强大,它的值可以有以下选择:
content:<string>|<uri>|attr(<identifier>)
使用content属性中的attr()值配合setAttribute()方法就可以实现自定义伪元素的内容。
IE8-浏览器需要在元素特性中出现data-beforeData(设置为空字符串即可),才有效果;其他浏览器无此问题。
<style>
#box:before{content: attr(data-beforeData);color: red;}
</style>
<!--为了兼容IE8-,需要在元素特性中设置 data-beforeData=""-->
<div id="box" data-beforeData="">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">添加伪元素</button>
<script>
btn.onclick = function(){
box.setAttribute('data-beforeData','前缀');
}
</script>
dataset
HTML5新增了dateset数据集特性,将元素特性和对象属性联系在了一起。
[注意]IE10-浏览器不支持。
如果不考虑兼容,同样可以实现dateset来实现,但是由于dataset的解释规则,元素特性的值不可以出现大写,需要进行局部修改。
经测试,IE11浏览器不支持使用dateset动态修改伪元素。
<style>
#box:before{content: attr(data-before);color: red;}
</style>
<div id="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">添加伪元素</button>
<script>
btn.onclick = function(){
box.dataset.before = '前缀';
}
</script>
04. 通过CSSRule对象添加样式
虽然伪元素的样式无法通过操作行间样式来直接添加,但是可以通过CSSRule对象通过操作内部样式表实现。
如果存在内部样式表,即存在<style>标签,则直接在<style>标签中添加样式;否则先新建<style>标签,再添加样式。
<div id="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">添加伪元素</button>
<script>
// 作为存在<style>标签的标记,1表示存在,0表示不存在
var mark = 0;
var tags = document.getElementsByTagName('*');
function addStyle(obj){
var str = '#box:before{content:"前缀";color: pink;}';
var sheet = obj.sheet || obj.styleSheet;
var rules = sheet.cssRules|| sheet.rules;
for(var i = 0,len = rules.length; i < len; i++){
//如果已经设置了:before伪元素的样式,就不再重复添加
if(/:before/.test(rules[i].selectorText)){
//obj.mark表示是否设置了:before伪元素的样式,1为已设置,0为未设置
obj.mark = 1;
break;
}
}
// 如果未设置伪元素样式
if(!obj.mark){
if(sheet.insertRule){
sheet.insertRule('#box:before{content:"前缀";color:green;}',0);
}else{
sheet.addRule('#box:before','content:"前缀";color:green;',0);
}
}
}
btn.onclick = function(){
for(var i = 0; i < tags.length; i++){
if(tags[i].nodeName == 'STYLE'){
mark = 1;
// 添加伪元素
addStyle(tags[i]);
break;
}
}
if(!mark){
// 新建<style>标签
var ele = document.createElement('style');
document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(ele);
// 添加伪元素
addStyle(ele);
}
}
</script>
02. 删除为元素
相比于新增伪元素来说,删除伪元素要困难一些。因为<style>元素中可能还有许多其他的样式,所以只能通过覆盖或删除指定样式来实现。
[1] 空样式覆盖
使用优先级更高的:before伪元素的空样式来覆盖原有样式。
<style>
#box:before{content:"前缀";color:green;}
.remove:before{content:""!important;}
</style>
<div id="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">删除伪元素</button>
<script>
btn.onclick = function(){
box.className = 'remove';
}
</script>
[2] 通过CSSRule对象删除指定
通过selectorText找出CSSRule对象中的:before伪元素的CSS规则。
[注意] 在IE8浏览器中,:before伪元素选择器文本会自动将冒号置为单冒号,而其他浏览器会自动将冒号置为双冒号。
然后使用deleteRule()方法或removeRule()方法删除指定样式。
<style>
#box::before{content:"前缀";color:green;}
</style>
<div id="box">测试文字</div>
<button id="btn">删除伪元素</button>
<script>
function deleteStyles(){
var sheet = document.styleSheets[0];
var rules = sheet.cssRules || sheet.rules;
for(var i = 0; i < rules.length; i++){
//找出伪元素
if(/#box:(:)?before/.test(rules[i].selectorText)){
if(sheet.deleteRule){
sheet.deleteRule(i);
//兼容IE8-浏览器
}else{
sheet.removeRule(i);
}
}
}
}
btn.onclick = function(){
deleteStyles();
}
</script>